NestJS 기초 사용 방법

NestJS 기초 사용 방법에 대해 설명하는 페이지입니다.
Environment
- Node.js v20.11.1
- @nestjs/cli v10.3.2
- reflect-metadata v0.2.2
목차
- 개요
- Step 1 - NestJS 애플리케이션 생성
- Step 2 - eslintrc 설정 파일 수정
- Step 3 - Folder Structure / Architecture 확인하기
- Step 4 - Blog API 만들기
- Step 5 - Postman으로 테스트하기
- Comments
개요
이번 글에서는 NestJS 기초 사용 방법에 대해 설명하도록 하겠습니다.
Step 1 - NestJS 애플리케이션 생성
다음 명령어를 입력하여 @nestjs.cli를 사용하여 NestJS 애플리케이션을 생성합니다.
npx @nestjs/cli new [프로젝트 이름]
명령어를 입력하면 어떤 패키지 매니저를 사용할 것인지를 결정해야 합니다. 저의 경우 npm을 선택하였습니다.
? Which package manager would you ❤️ to use? npm
Step 2 - eslintrc 설정 파일 수정
자신이 사용하는 운영체제에 따라 다음과 같이 Delete ␍ eslint (prettier/prettier) 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
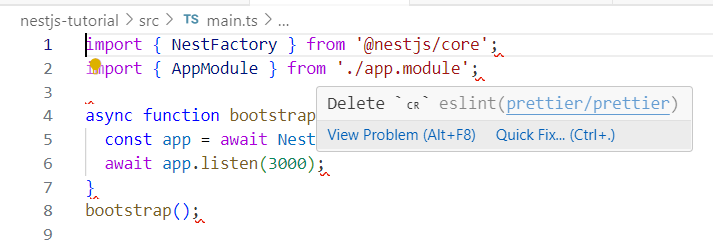
이 오류가 발생하는 경우 .eslintrc.js 파일을 열고 다음과 같이 endOfLine에 내용을 추가하거나 변경하면 됩니다.
rules: {
(...)
'prettier/prettier': [
'error',
{
endOfLine: 'auto',
},
],
},
Step 3 - Folder Structure / Architecture 확인하기
nest-cli로 생성한 프로젝트 구조는 다음과 같습니다.
├── src
| ├── app.controller.spec.ts // 컨트롤러 테스트 코드
| ├── app.controller.ts // 컨트롤러
| ├── app.module.ts // 모듈
| ├── app.service.ts // 서비스
| └── main.ts // 서비스 메인 파일
├── .gitignore // git 버전 관리에서 제외할 목록 지정
├── .prettierrc // 코드 포매팅 관련 설정 파일
├── nest-cli.json // nest-cli 설정
└── (...)
NestJS의 Naming 규칙
NestJS의 Naming Convention은 다음과 같습니다.
- 파일명은
.으로 연결하며, 모듈이 둘 이상의 단어로 구성되어 있으면대시로 연결합니다.// <모듈명>.<컴포넌트명>.ts blog.controller.ts my-first.controller.ts - 클래스명은
Pascal Case로 표기합니다.// <모듈명><컴포넌트명> BlogController - 같은 디렉토리에 있는 클래스는 index.ts를 통해서 임포트하는 것이 권장됩니다.
- 인터페이스를 사용해서 타입을 정의하고 구체적인 내용을 클래스를 만들어 인터페이스를 상속하는 방식으로 작성합니다.
main.ts
main.ts 파일은 NestJS 서버의 시작점이 되는 파일입니다. NestJS에서는 진입점을 bootstrap()으로 하는 것이 관례입니다.
import { NestFactory } from "@nestjs/core";
import { AppModule } from "./app.module";
// NestJS를 실행시키는 함수
// NestJS에서는 진입점을 bootstrap()으로 이름 짓는 것이 관례이다.
async function bootstrap() {
// NestFactory를 사용해서 NestApplication 객체 생성
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
// 3000번 포트로 서버 기동
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
모듈명.controller.ts
컨트롤러는 유저가 보낸 HTTP 요청을 어떤 코드에서 처리할지 결정하는 역할을 합니다.
import { Controller, Get } from "@nestjs/common";
import { AppService } from "./app.service";
@Controller() // 컨트롤러 데코레이터
export class AppController {
// 외부에서 사용하므로 export를 붙임.
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) {}
@Get() // GET 요청 처리 데코레이터
getHello(): string {
return this.appService.getHello();
}
}
모듈명.service.ts
서비스는 비즈니스 로직을 담는 파일입니다.
import { Injectable } from "@nestjs/common";
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
getHello(): string {
return "Hello World! 안녕하세요!";
}
}
모듈명.module.ts
모듈은 수평적으로 흩어진 Provider와 Controller들을 논리적인 기능이나 도메인에 따라 하나로 묶어주는 역할을 하며, 재사용성을 높여줍니다.
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { AppController } from "./app.controller";
import { AppService } from "./app.service";
import { BlogModule } from "./blog/blog.module";
// 모듈 데코레이터
@Module({
imports: [],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}
Step 4 - Blog API 만들기
데이터베이스를 사용하지 않는 간단한 Blog API를 만들어 보겠습니다. 먼저 다음과 같이 모듈 단위로 애플리케이션을 구성합니다.
├── src
| ├── app.controller.spec.ts
| ├── app.controller.ts
| ├── app.module.ts
| ├── app.service.ts
| ├── main.ts
| └── modules
| └── blog
| ├── blog.controller.ts
| ├── blog.module.ts
| ├── blog.service.ts
| └── dtos
| └── blog.dto.ts
└── (...)
modules 디렉토리에 도메인별 모듈을 저장합니다. 각 모듈은 해당 기능과 관련된 컨트롤러, 서비스, DTO 등을 포함합니다.
blog.controller.ts
import {
Body,
Controller,
Delete,
Get,
Param,
Post,
Put,
} from "@nestjs/common";
import { BlogService } from "./blog.service";
import { PostDto } from "./dtos/blog.dto";
@Controller("blog") // 클래스에 붙이는 Controller 데코레이터
export class BlogController {
constructor(private readonly blogService: BlogService) {}
@Get() // GET 요청 처리하기
getAllPost() {
console.log("모든 게시글 가져오기");
return this.blogService.getAllPosts();
}
@Post() // POST 요청 처리하기
createPost(@Body() postDto: PostDto) {
// HTTP 요청의 body 내용을 post에 할당
console.log("게시글 작성");
this.blogService.createPost(postDto);
return "success";
}
@Get("/:id") // GET 요청에 URL 매개변수에 id가 있는 요청 처리
getPost(@Param("id") id: string) {
console.log("게시글 하나 가져오기");
return this.blogService.getPost(id);
}
@Delete("/:id") // DELETE 방식에 URL 매개변수로 id가 있는 요청 처리
deletePost(@Param("id") id: string) {
console.log("게시글 삭제");
this.blogService.delete(id);
return "success";
}
@Put("/:id") // PUT 방식에 URL 매개변수로 전달된 id가 있는 요청 처리
updatePost(@Param("id") id: string, @Body() postDto: PostDto) {
console.log("게시글 업데이트", id, postDto);
return this.blogService.updatePost(id, postDto);
}
}
위의 코드에서 Get, Post, Delete, Put 등의 데코레이터는 모두 함수에 붙이는 것으로, HTTP 요청 방식에 따라 해당 데코레이터가 붙은 함수를 실행합니다. @Body는 함수의 body로 오는 값을 매개변수에 할당하며, @Param은 URL param의 값을 함수 매개변수에 할당합니다.
blog.service.ts
import { Injectable } from "@nestjs/common";
import { PostDto } from "./dtos/blog.dto";
@Injectable()
export class BlogService {
posts: PostDto[] = []; // 게시글 배열 선언
// 모든 게시글 가져오기
getAllPosts() {
return this.posts;
}
// 게시글 작성
createPost(postDto: PostDto) {
const id = this.posts.length + 1;
this.posts.push({
id: id.toString(),
...postDto,
createdAt: new Date(),
});
}
// 게시글 하나 가져오기
getPost(id: string) {
const post = this.posts.find((post) => post.id === id);
console.log(post);
return post;
}
// 게시글 삭제
delete(id: string) {
const filteredPosts = this.posts.filter((post) => post.id !== id);
this.posts = [...filteredPosts];
}
// 게시글 업데이트
updatePost(id: string, postDto: PostDto) {
const updateIdx = this.posts.findIndex((post) => post.id === id);
const updatePost = { id, ...postDto, updatedAt: new Date() };
this.posts[updateIdx] = updatePost;
return updatePost;
}
}
Blog API 로직을 위와 같이 service 파일에 작성합니다.
blog.module.ts
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { BlogController } from "./blog.controller";
import { BlogService } from "./blog.service";
@Module({
imports: [],
controllers: [BlogController],
providers: [BlogService],
exports: [],
})
export class BlogModule {}
위와 같이 blog 컨트롤러와 서비스를 모듈 파일에 선언합니다.
blog.dto.ts
// 게시글의 타입을 인터페이스로 정의
export interface PostDto {
id: string;
title: string;
content: string;
name: string;
createdAt: Date;
updatedAt?: Date; // 수정 일시는 필수가 아님.
}
Dto란 data transfer object의 약자입니다. 주로 데이터 전송을 위한 객체로, 애플리케이션 계층 간에 데이터를 주고받을 때 사용됩니다. 타입스크립트에서는 데이터만 가지고 있는 타입을 선언할 때 클래스보다는 인터페이스를 많이 사용합니다.
app.module.ts
작성한 Blog 모듈을 사용하기 위해 다음과 같이 app 디렉토리의 최상위 모듈 파일에 모듈을 import 합니다.
import { Module } from "@nestjs/common";
import { AppController } from "./app.controller";
import { AppService } from "./app.service";
import { BlogModule } from "./modules/blog/blog.module";
// 모듈 데코레이터
@Module({
imports: [BlogModule],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}
Step 5 - Postman으로 테스트하기
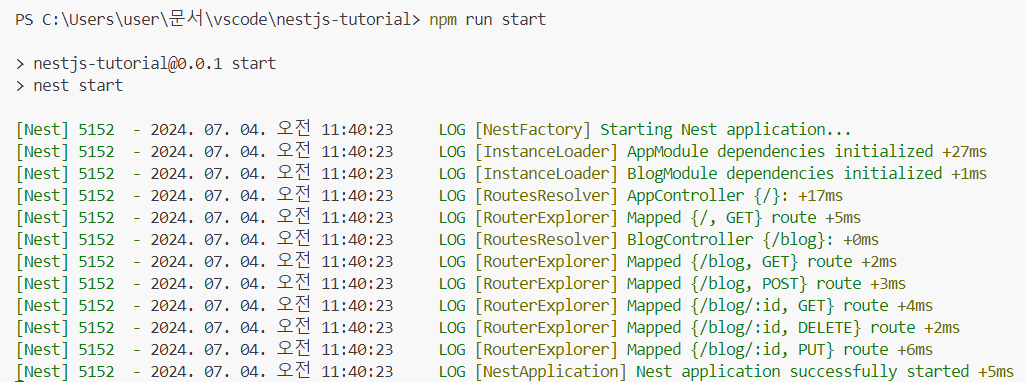
서버 실행하기
Postman을 사용하여 위의 API가 잘 작동하는지 확인하도록 하겠습니다. 먼저 다음 명령어를 입력하여 서버를 시작합니다.
npm run start
서버를 시작하는 방법은 위 방법 외에도 다음과 같은 방법이 있습니다. 이에 대해선 package.json 파일을 참고하시길 바랍니다.
npm run start // 서버 시작
npm run start:dev // development 모드로 실행할 때 사용
npm run start:prod // production 모드로 실행할 때 사용
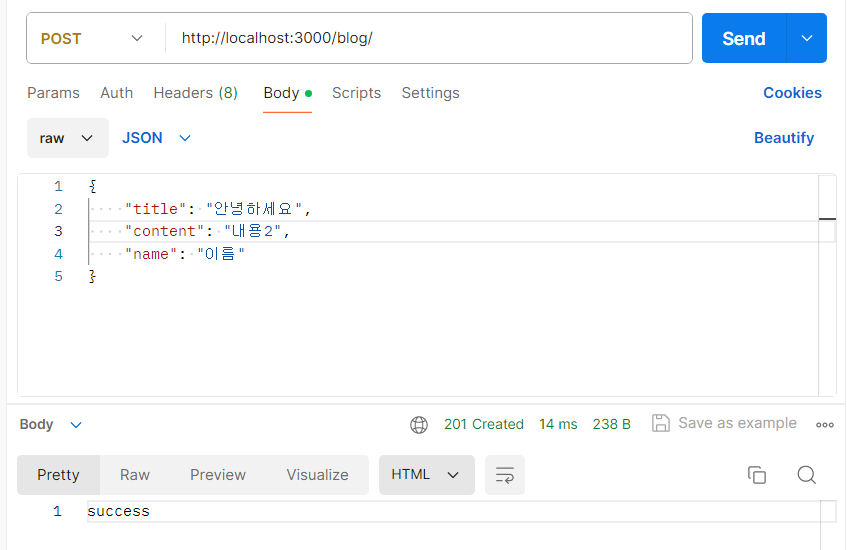
게시글 작성
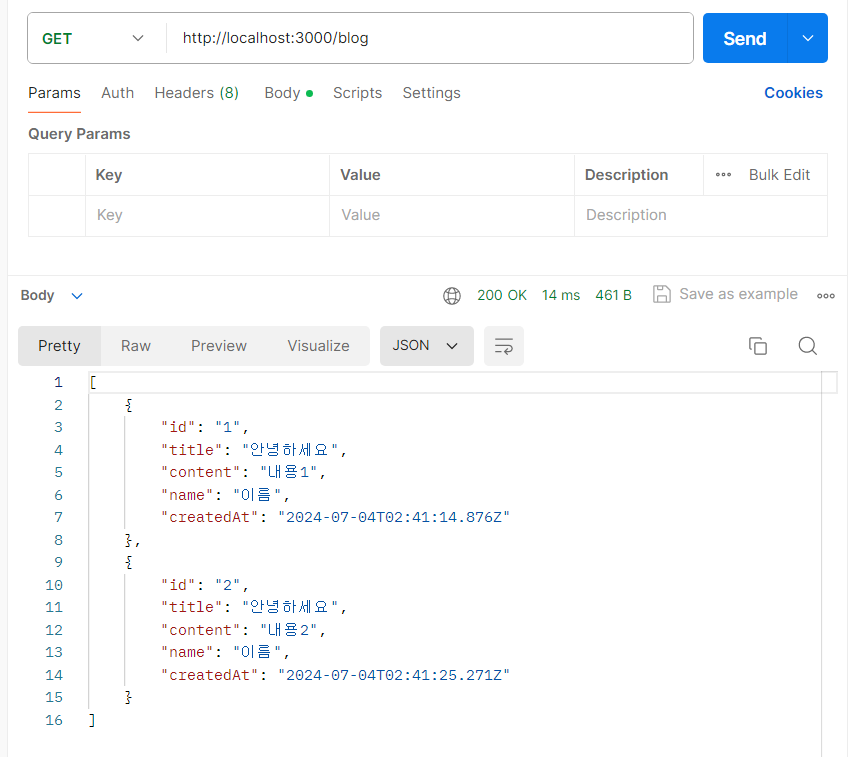
게시글 조회